
By Mike Powell, CEO, Rapid Addition.
In previous blogs, we’ve explored the factors driving capital markets’ embrace of cloud technologies, the benefits firms are already enjoying from making the move, and some of the obstacles that can derail a cloud migration strategy.
What’s clear is that for capital markets, cloud isn’t a panacea but rather an increasingly important tool in the kitbag of a CTO. It adds value in some areas but is inappropriate for others. In a survey of 20 leading capital markets organisations commissioned by Rapid Addition and conducted by A-Team Group, we asked which functional areas represent ‘low-hanging fruit’ and which just aren’t applicable either now or in future.
To some extent, the functional areas identified as potentially ‘in’ or ‘out’ of scope by the survey aren’t surprising (See Chart 1, below), suggesting that trading firms want to retain control over the highly latency-sensitive components of trading workflow to ensure deterministic performance.
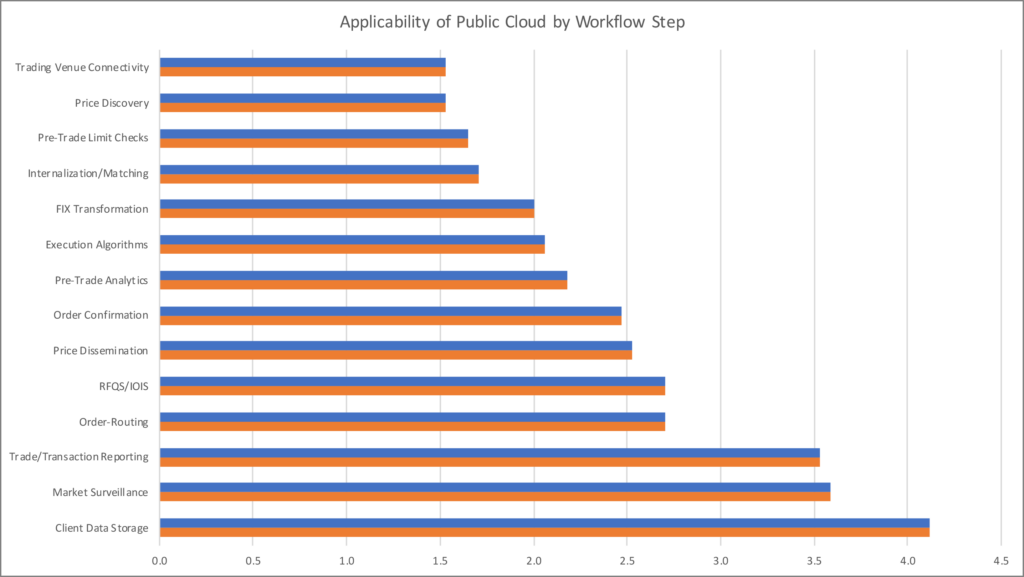
And yet, some respondents described projects that appear to break with this view. For instance, one firm said it was deploying a global equity order routing network in the cloud. While this is less latency sensitive than trade execution, it is a critical real-time link in the trading value chain, suggesting firms may be reaching further than is apparent on the surface.
Respondents also suggested that certain asset classes were fundamentally better suited to cloud-based applications than others (See Chart 2, below). This tended to correlate with the latency profile, with less liquid and more opaque asset classes like OTC derivatives and certain fixed-income securities perceived as more cloud-ready than say listed equity and derivatives markets (which, with a central limit order book model, is where we see significant investment in co-lo, hardware acceleration and other high-performance infrastructure).
Considering the lengths that exchanges go to not only optimise performance but also ensure a level playing field, for instance through equidistant cabling within their co-lo facilities, it is hard to see how public cloud is suitable in its current state. But consider a less liquid emerging or frontier market or an exchange model built only on periodic auctions and suddenly the need for very low latency performance dissipates.
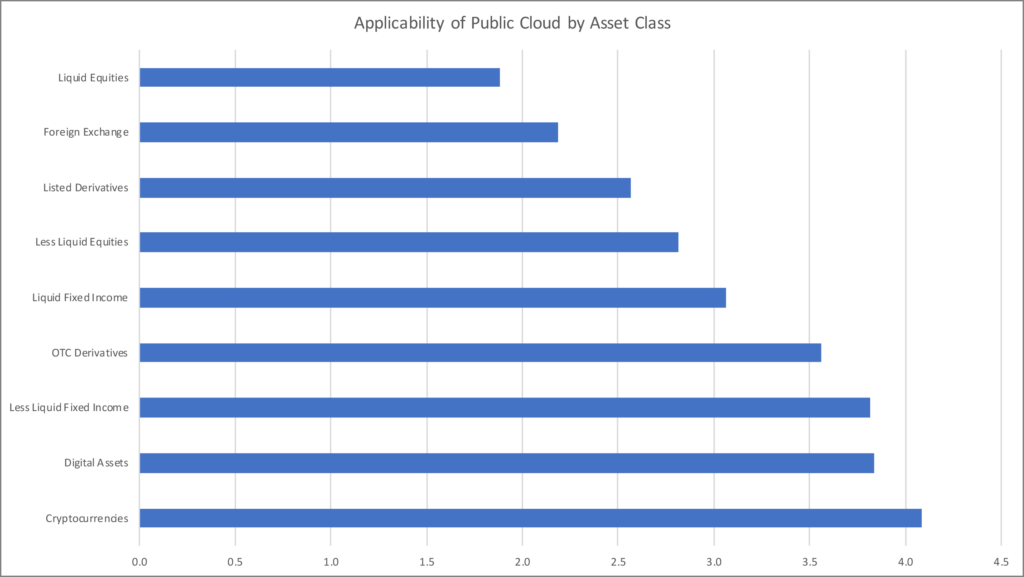
Of course, the ‘green-field’ site’ opportunity of digital assets and cryptocurrencies is seen as a prime example of how to build workflows in a cloud-native environment. But even practitioners in traditional asset classes see cloud as an opportunity to rethink existing practices. One major global equities exchange described using the public cloud to spin up a new area of business, initially for testing but ultimately for full-production trading.
Ultimately it depends on how you frame the question and what is your definition of electronic trading workflow. Which link in the trading value chain are you looking at? They are not all equally performance-sensitive and given increasing cost and competitive pressures, is a more targeted view of cloud applicability beneficial?
An order is not the same as an execution, so does sending a parent order from London to Johannesburg have the same performance requirement as the execution platform of the receiving broker? Or is there the same latency requirement to send a trade confirmation as there is to run a pre-trade risk check? Assuming you agree the answer is ‘no’, we can start to see how cloud can permeate certain elements of trading workflow and drive potential efficiencies.
When asset class, market type and structure are also factored into the discussion it suggests that there is plenty of scope to leverage cloud in trading. Increasingly CTOs understand that there is no one-size-fits-all design for infrastructure – their role is to apply the most suitable technologies to address business requirements within the constraints of budgets and regulations. Cloud is a key part of the toolset to help their organisations move faster in response to changing client and market needs.
In our next and final blog in this series, we’ll look at what the future holds for capital markets and the public cloud. In the meantime, you can download the full report here.
Subscribe to our newsletter




